Mammograms and More: Breast Cancer Screening Guidelines
Conflicting guidelines on the age to start mammograms might have you scratching your head. Start at 40 years old, or 50? Every year, every other?
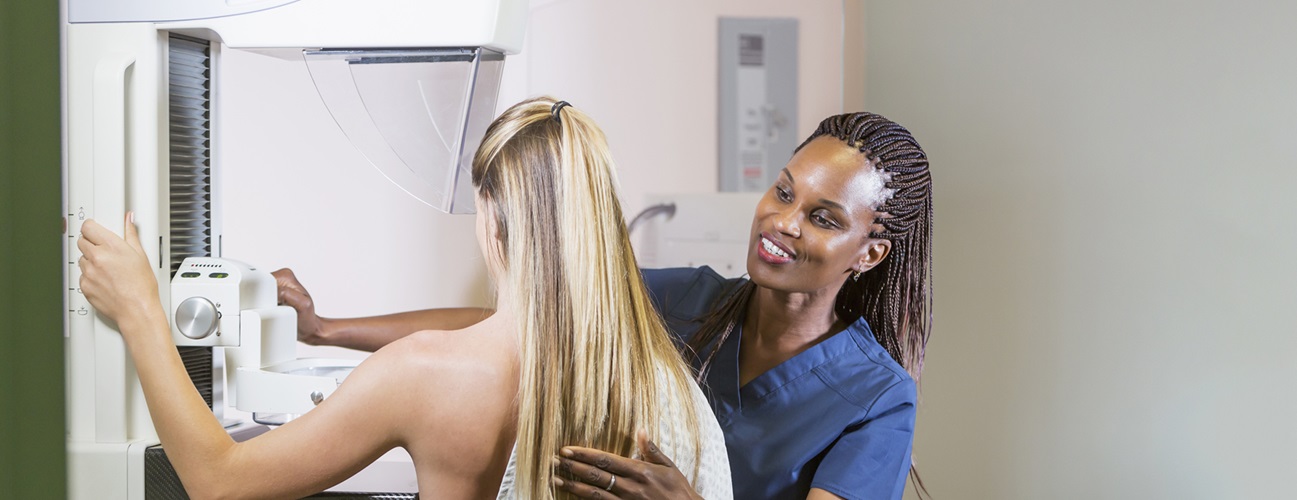
Johns Hopkins Medicine, along with the American College of Radiology (ACR) and the Society of Breast Imaging (SBI) maintain their recommendation for women at average risk to have routine annual screening from 40 through 80 years of age. Women with specific risk factors may start earlier than age 40.
You should discuss your individual screening options with your doctor.
Why should you start having mammograms at 40?

An annual screening mammogram is your best defense against breast cancer. Mammography detects most cancers in women who show no symptoms or who are considered low risk. False alarms can be stressful, but the fact is that early detection saves lives. One in six breast cancers occurs in women ages 40 to 49.
A yearly mammogram for women 40 and older helps to detect breast cancer earlier, when it is most treatable, leading to less aggressive treatment and a higher rate of survival.
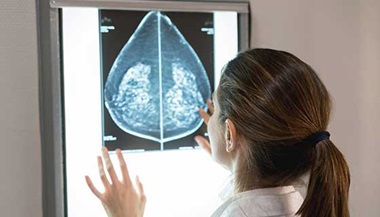
To reduce the risk of false positives, patients can request tomosynthesis, otherwise known as 3-D mammograms. (Check with your insurance plan about coverage.) “3-D mammography provides a clearer image of each layer of the breast, which provides greater visibility for the radiologist. This results in a 20 to 40 percent less chance of being called back for a second look, and detects more cancers.”
How do I schedule my appointment?
You can schedule your yearly exam without a doctor’s prescription or a screening mammogram order form. Women can self-refer to make an appointment for their annual mammogram for earlier detection of breast cancer.
Find an Imaging Location

Breast Cancer Screening Recommendations
The following are the recommended guidelines for breast cancer screening by age and risk factor:
Beginning at 16 to 18:
- Breast self-exam
Breast cancer is one of the few cancers that can sometimes be felt. It is important to become accustomed to how your breasts naturally feel so that you can recognize any abnormalities. Breast tissue can be lumpy, but if you think you feel something abnormal, you should contact your doctor.
20 onward:
- Annual clinical breast exam
This is typically conducted at your yearly gynecological or physical exam.
40 onward:
- Annual clinical breast exam
- Annual mammogram
There is no recommended age at which you should stop receiving annual mammograms, unless you have less than five years of life expectancy due to old age or other illness.
40 onward, with high-risk factors
- Annual clinical breast exam
- Annual mammogram
- Breast MRI (or breast ultrasound for those who cannot have an MRI)