Hypopharyngeal Cancer
Reviewed By:
What is hypopharyngeal cancer?
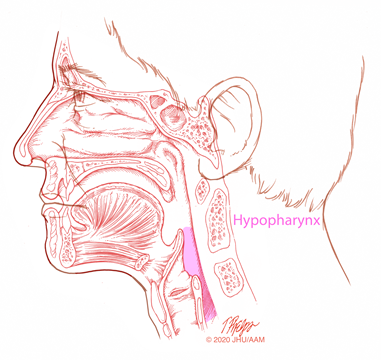
Hypopharyngeal cancer is an abnormal growth of cancer cells in a region of the lower throat known as the hypopharynx. The hypopharynx lies within the lower neck and throat behind the voice box just above the inlet to the esophagus. The majority of these cancers (~95%) represent a type of cancer known as squamous cell carcinoma which is usually smoking-related but other rarer types of cancer in this region can also occur and are generally not smoking-related.
What are symptoms of hypopharyngeal cancer?
Symptoms for hypopharyngeal cancer can vary from patient to patient and can often go unnoticed for some time. Common symptoms include:
- Difficulty and/or pain with swallowing
- Unexplained ear discomfort
- Hoarse voice
- Difficulty breathing
- Painless lump or mass on the neck
- Coughing blood
Johns Hopkins Head and Neck Cancer Specialists

Our head and neck surgeons and speech-language pathologists take a proactive approach to cancer treatment. Meet the Johns Hopkins specialists who will work closely with you during your journey.
How is hypopharyngeal cancer diagnosed?
Your head and neck surgeon will visualize the hypopharynx using a simple in-office procedure called flexible fiberoptic endoscopy. A small flexible scope is inserted into the nose to help visualize tumor masses involving the hypopharynx. Local numbing medicine is given through the nose to make the procedure comfortable and painless for the patient. Further imaging (CT scan, MRI or PET scans) may be needed to better characterize the extent of the tumor. A biopsy is then usually performed in the operating room under general anesthesia to confirm the diagnosis and examine the tumor more closely.
How is hypopharyngeal cancer treated?
Treatment options depend on how large the tumor is or if it has spread to other parts of the body. It may include some or a combination of these depending on the extent of the tumor:
- Surgery
- Radiation therapy
- Chemotherapy
- Immunotherapy medications that can activate the body’s immune system to fight the cancer.
A team-based approach involving surgeons, radiation oncologists, medical oncologists, speech language pathologists, and others is used to formulate the best treatment plan for each individual patient to control the tumor and promote the best quality of life possible after treatment.
Johns Hopkins Head and Neck Cancer Surgery

Our team offers comprehensive treatments for cancers affecting the nasal passages, sinuses, the throat and nearby areas. Our head and neck surgeons work closely with medical and radiation oncologists, endocrinologists and other specialists to provide well-rounded care.