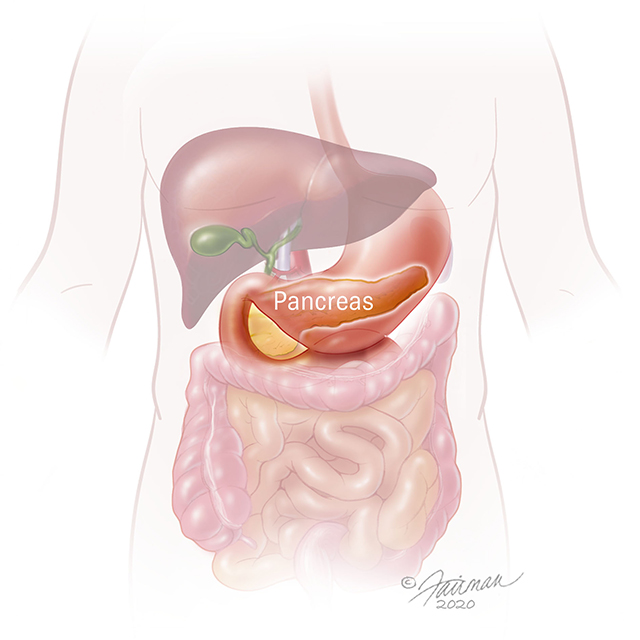
Hepatologist Victor Chen and colleagues at Johns Hopkins want to change the way Americans think about alcohol use disorder and liver transplants.
For decades, transplant centers in the United States have followed a practice that requires patients to abstain from drinking alcohol for six months to be eligible for a liver transplant.
With cadaveric donor livers in high demand, most transplant centers put patients whose liver damage stems from active alcohol use at the bottom of their priority lists — if they consider them at all. No matter the severity of the liver disease or how long the patient is expected to survive without a transplant, the majority of U.S. centers will not perform the procedure.
Johns Hopkins is one of the few centers in the United States that regularly transplants livers into patients with alcohol-related liver disease whose sobriety doesn’t reach the six-month threshold.
Chen believes what puts Johns Hopkins ahead of most American transplant centers in this area is the collaboration between hepatologists, surgeons, social workers and addiction specialists.
“We use a combination of behavioral therapy and medicine to help people avoid alcohol after transplant,” he says.
Chen says that, when he talks to medical students about the approach, many of them cannot understand why the policy would be controversial.
“A lot of times, I’ll get this look from them that says, ‘why are we even talking about this?’”
In 2011, a European team of hepatologists challenged the notion of the six-month sobriety policy. Soon after, the practice of transplant for patients with alcohol-damaged livers became more common across the continent.
But in the United States, the policy remains the norm.
“We were one of the very first transplant centers in the nation to say ‘maybe there’s something to this,’” says Chen. “We started exploring and incorporating it into our own culture.”
Today, according to Chen, Johns Hopkins performs about 25 liver transplants a year for patients who would not otherwise get the lifesaving surgery.
Surgeon Andrew Cameron is chief of the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine’s Division of Transplantation and surgical director of liver transplantation.
He says that, while the six-month guideline isn’t a factor at Johns Hopkins, candidates do need to meet certain qualifications. Among them is the patients’ insight into their own alcoholism.
“This is for people for whom there is evidence of an ability to turn their life around,” Cameron says. “Before we agree to the transplant, we look at the patient’s family or other support systems and the patient’s commitment to change.”
Funders have taken note of the work taking place at Johns Hopkins. Last year, Cameron received an $8.4 million grant from the National Institutes of Health to study alcoholic hepatitis. Chen also secured an NIH grant that began in July 2020. His five-year, $1 million funding supports research into transplant candidate selection for alcohol-related liver disease.
Part of Cameron’s funding allows his team to explore solutions to help transplant patients avoid a recurrence of the condition. “A liver transplant won’t cure alcohol use disorder,” Cameron acknowledges. “We’re exploring behavioral and pharmacologic interventions to give our patients their best shot at a healthy life.”