Cell’s ‘Garbage Disposal’ May Have Another Role: Helping Neurons Near Skin Sense the Environment
04/12/2024
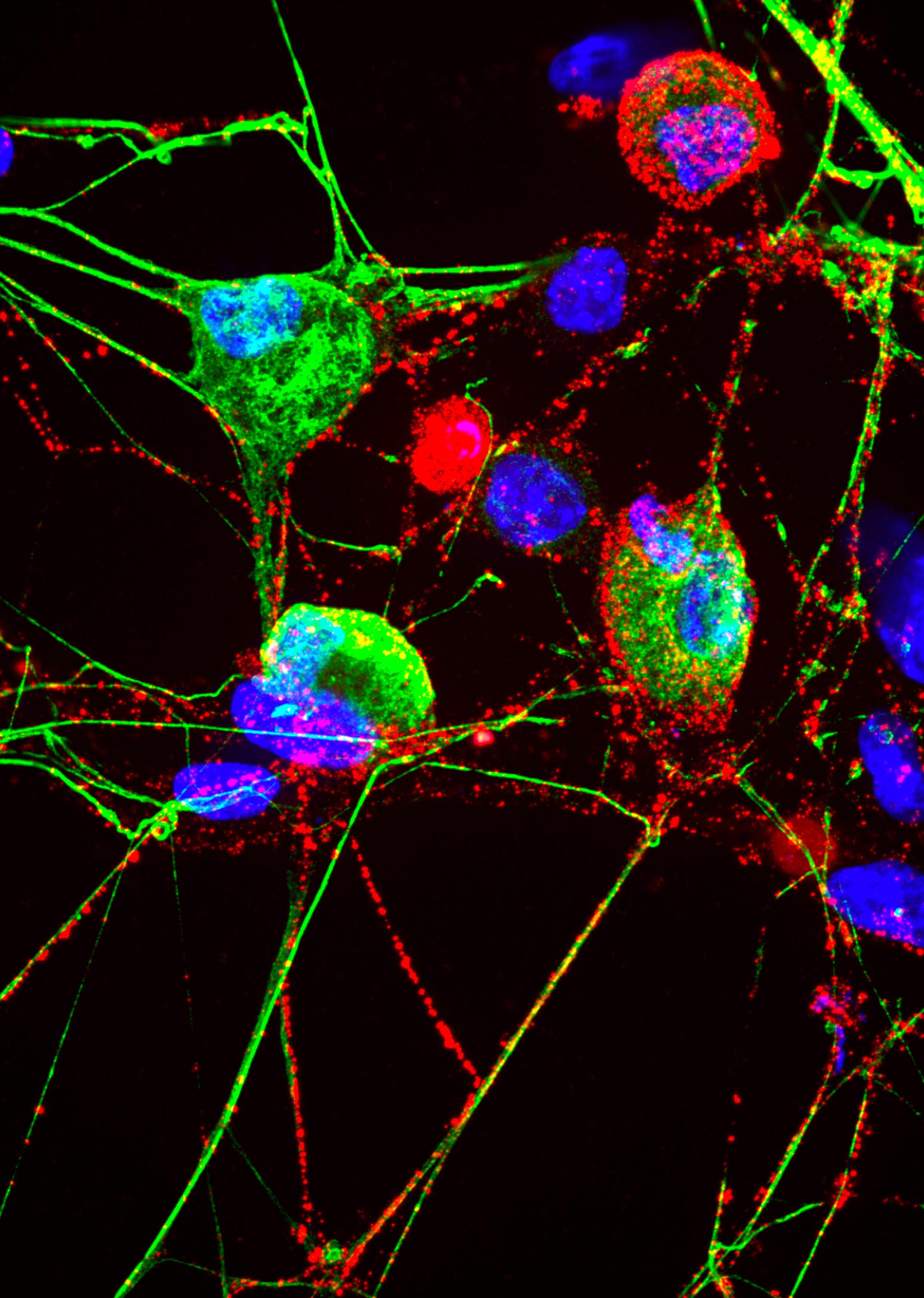
The typical job of the proteasome, the garbage disposal of the cell, is to grind down proteins into smaller bits and recycle some of those bits and parts. That’s still the case, for the most part, but, Johns Hopkins Medicine researchers, studying nerve cells grown in the lab and mice, say that the proteasome’s role may go well beyond that.
Its additional role, say the researchers, may shift from trash sorter to signal messenger in dorsal root ganglion neurons — cells that convey sensory signals from nerve cells close to the skin to the central nervous system.
Results of their experiments, published April 12 in Cell Reports, show that proteasomes may help those specialized neurons sense the surrounding environment, send signals to each other and potentially differentiate between sensing pain and itch, a finding that could help scientists better understand these sensory processes and new targets for treating pain and other sensory problems.
“Neurons live next to each other for a long time, and they need ways to communicate with each other about what they’re doing and who they are,” says Seth S. Margolis, Ph.D., associate professor of biological chemistry at the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine. “Proteasomes in the membrane of neurons may help the cells fine tune this messaging process.”
“Proteasomes are more complicated than they appear,” says Margolis. He and his colleagues first found proteasomes in the plasma membranes of central nervous system neurons in mice in 2017, which they dubbed neuronal membrane proteasomes, and have continued studying how these special proteasomes promote messaging, or crosstalk, among neurons.
At the time, Margolis’ focus was on the central nervous system, encompassing the brain and spinal cord. But later, he collaborated with neurobiologist Eric Villalón Landeros, Ph.D., postdoctoral fellow in Margolis’ laboratory at Johns Hopkins, whose work focuses on the peripheral nervous system, the network of neurons running through the rest of the body, closer to the skin, capturing sensory information from the environment.
Margolis and Villalón Landeros wondered whether proteasomes could be found in peripheral neurons, and if so, what they might do.
Using mouse antibodies that glom on to proteasomes, and other methods, the investigators found the proteasomes on the surface of neurons in the spinal cord, dorsal root ganglia, sciatic nerve and peripheral nerves innervating skin.
The researchers were also able to find proteasomes in the same type of peripheral neurons grown in laboratory culture dishes.
To understand the proteasome’s function in peripheral sensory neurons, the researchers gave mice biotin-epoxomicin, a cell membrane-impermeable proteasome inhibitor that blocks the function of neuronal membrane proteasomes. Then, they performed classic sensory tests.
The researchers found that the mice that got injections of the proteasome-blocking drug biotin-epoxomicin on one side of the body were between 25% to 50% slower than the other side to respond to sensory tests.
“This suggests that membrane proteasomes are important for sensation, and they must be facilitating this at the signaling level,” says Margolis.
The researchers used single cell sequencing technology to determine that membrane proteasomes were expressed in a subpopulation of neurons involved in itch sensation and known to be sensitive to histamine, an immune system compound that launches an animal’s (including human’s) response to allergens.
In laboratory culture dishes, the researchers stimulated both itch-related and non-itch related neurons and blocked their membrane proteasomes with biotin-epoxomicin. This resulted in changes to activity in all of the cells. “Blocking proteasomes seems to have an activity-modulatory effect across all the cells, despite being expressed in a subpopulation, suggesting that proteasomes facilitate a kind of cross talk between these cells,” says Margolis.
Proteasome blockers, including one called Velcade, are currently used to treat certain types of cancer.
Villalón Landeros and Margolis plan to continue working together to determine how neuronal membrane proteasomes function in sensory neurons and in sensing pain versus itch. “We want to see if we can manipulate neuronal membrane proteasomes to have a different outcome on pain and itch sensation,” says Villalón Landeros.
Additional scientists who contributed to the research are Samuel Kho, Taylor Church, Anna Brennan, Fulya Türker, Michael Delannoy and Michael Caterina from Johns Hopkins.
Funding for the research was provided by the National Institutes of Health (F32NS119202, R01 NS110754) and a Merkin Peripheral Neuropathy and Nerve Regeneration Center grant.