Clavicle Fracture Open Reduction and Internal Fixation
What is clavicle fracture open reduction and internal fixation?
Open reduction and internal fixation (ORIF) is a type of surgery used to stabilize and heal a broken bone. You might need this procedure to treat your broken collarbone (clavicle).
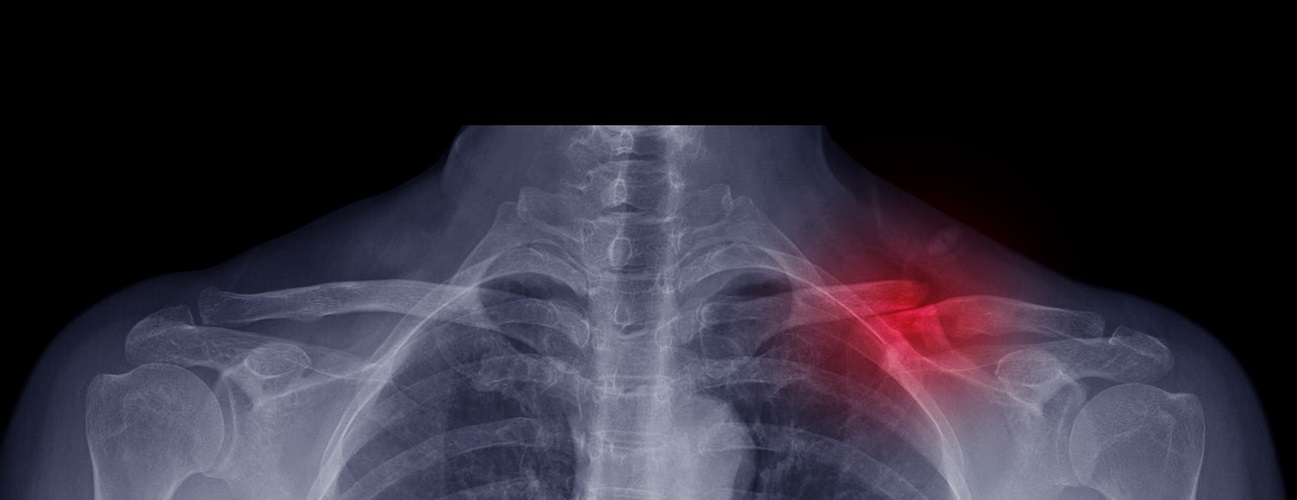
The clavicle is a long thin bone located between your ribcage and the shoulder blade. Different kinds of injury can damage this bone, causing it to fracture into two or more pieces. Most often, this happens along the middle of the bone. Occasionally, the bone breaks near where it attaches to the ribcage, or near where it attaches to the shoulder blade.
In certain types of clavicle fractures, your clavicle has broken, but its pieces still line up correctly. In other types of fractures (displaced fractures), the injury moves the bone fragments out of alignment.
If you fracture your clavicle, you might need ORIF to bring your bones back into place and help them heal. During an open reduction, orthopedic surgeons reposition your bone pieces surgically back into their proper alignment. In a closed reduction, a doctor physically moves the bones back into place without surgically exposing the bone.
Internal fixation refers to the method of physically reconnecting the bones. This method uses special screws, plates, wires, or nails to position the bones correctly. This prevents the bones from healing abnormally. The entire operation usually takes place while you are asleep under general anesthesia.
Why might I need a clavicle fracture open reduction and internal fixation?
Certain medical conditions may make fracturing your clavicle more likely. For example, osteoporosis increases the risk of clavicle fracture in many older adults.
You may fracture your clavicle from a direct blow to the shoulder, such as while playing a sport or if you're in a car wreck. Falling on an outstretched arm may also fracture a clavicle. In some cases, a newborn baby will fracture the clavicle during the birth process.
Not everyone with a fractured clavicle needs ORIF. In fact, most people don’t. If possible, your doctor will treat your clavicle fracture with more conservative treatments, like pain medicines, splints, and slings.
You probably won’t need ORIF unless there is some reason your fracture might not heal normally with these conservative treatments. You may need ORIF if:
- The pieces of your clavicle are significantly out of alignment
- Your clavicle broke through the skin
- Your clavicle broke into several pieces
In these cases, ORIF can position your bones back into their proper configuration. This significantly increases the chance that your bone will heal properly. In some cases, you might opt not to have ORIF even if your clavicle is significantly out of alignment, because the bone often heals correctly on its own. Your doctor can talk to you about the risks and benefits of ORIF or discuss other, more conservative treatments for your situation.
What are the risks for clavicle fracture open reduction and internal fixation?
Most people do very well with ORIF for their clavicle fracture. However, some rare complications do sometimes occur. Possible complications include:
- Broken screws or plates
- Infection
- Damage to an artery or vein
- Nerve damage
- Bone misalignment
- Injury to the lung
- Complications from anesthesia
There is also a risk that the fracture won’t heal properly, and you’ll need repeat surgery.
Your own risk of complications may vary according to your age, the anatomy of your clavicle fracture, and your other medical conditions. For example, people with low bone mass or diabetes may be at higher risk of complications. Being a smoker may also increase your risk. Ask your doctor about the risks that most apply to you.
How do I prepare for a clavicle fracture open reduction and internal fixation?
ORIF often takes place as an emergency or urgent procedure. Before your procedure, a healthcare professional will take your medical history and do a physical exam. You’ll need an X-ray of your clavicle. Tell your doctor about all the medicines you take, including over-the-counter medicines like aspirin. Also, let your doctor know the last time you ate.
In some cases, your doctors might perform your ORIF as a planned procedure. If this is the case, talk to your doctor about how to prepare for the procedure. Ask whether you should stop taking any medicines ahead of time, like blood thinners. You’ll need to avoid food and drink after midnight the night before your procedure.
What happens during a clavicle fracture open reduction and internal fixation?
Your doctor can help explain the details of your particular surgery. The details of your surgery will depend on the location and severity of your injury. An orthopedic surgeon and a team of specialized healthcare professionals will do the procedure. The whole operation may take a couple of hours. In general, you can expect the following:
- You will receive general anesthesia to make you sleep through the operation so that you won’t feel any pain or discomfort. (Or, you may receive local anesthesia and a medicine to help you relax.)
- A healthcare professional will carefully monitor your vital signs, such as your heart rate and blood pressure, during the operation. You may have a breathing tube placed down your throat during the operation to help you breathe.
- After cleaning the affected area, your surgeon will make an incision through the skin and muscle near your clavicle.
- Your surgeon will bring the pieces of your clavicle back into alignment (reduction).
- Next, your surgeon will secure the pieces of clavicle to each other (fixation). To do this, he or she may use screws, metal plates, wires, and pins. (Ask what the surgeon will use in your case.)
- Your doctor may make other necessary repairs.
- After the team has secured the bone, your surgeon will surgically close the layers of skin and muscle around your clavicle.
What happens after a clavicle fracture open reduction and internal fixation?
Talk to your doctor about what you can expect after your surgery. You may have some pain after your procedure, but pain medicine may help to reduce the pain. You should be able to resume a normal diet fairly quickly. You will probably need an imaging procedure, like an X-ray, to make sure that your surgery was successful. Depending on the extent of your injury and your other medical conditions, you may be able to go home the same day.
For a while after your surgery, you’ll need to keep your arm immobile. Often, this means that you will need to wear your arm in a sling for several weeks. You’ll receive instructions about how you can move your arm.
Your doctor might give you other instructions about caring for your clavicle, like applying ice. Follow all your doctor’s instructions carefully. Your doctor might not want you to take certain over-the-counter medicine for pain, because some of these can interfere with bone healing. Your doctor may advise you to eat a diet high in calcium and vitamin D as your bone heals.
You might have some draining of fluid from your incision. This is normal. Let your doctor know right away if:
- You see an increase in redness, swelling, or draining from your incision
- You have a high fever or chills
- You have severe pain
- You have loss of feeling anywhere in your body
Make sure to keep all of your follow-up appointments. You may need to have your stitches or staples removed a week or so after your surgery.
At some point, you may need physical therapy to restore strength and flexibility to your muscles. Doing your exercises as prescribed can improve your chances of a full recovery. Most people are able to return to all their normal activities within a few months.
Next steps
Before you agree to the test or the procedure make sure you know:
- The name of the test or procedure
- The reason you are having the test or procedure
- What results to expect and what they mean
- The risks and benefits of the test or procedure
- What the possible side effects or complications are
- When and where you are to have the test or procedure
- Who will do the test or procedure and what that person’s qualifications are
- What would happen if you did not have the test or procedure
- Any alternative tests or procedures to think about
- When and how will you get the results
- Who to call after the test or procedure if you have questions or problems
- How much will you have to pay for the test or procedure