Adrenoleukodystrophy (ALD)
Featured Expert:
What is ALD?
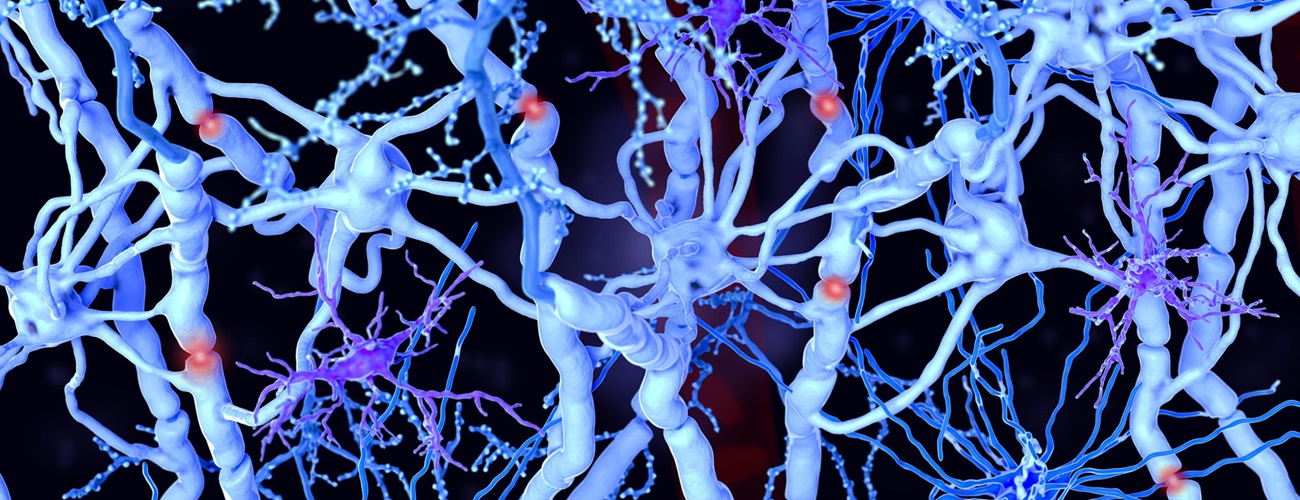
Adrenoleukodystrophy (ALD) is a genetic condition that damages the membrane (myelin sheath) that covers nerve cells in the brain and spinal cord. Myelin acts as insulation around the nerve fibers. When this insolating layer is damaged, nerve signals from the brain cannot communicate across the body properly, causing impaired bodily functions or paralysis.
ALD prevents the body from breaking down very long chain fatty acids (VLCFAs), causing these fatty acid chains to build up in the brain, nervous system and adrenal gland. The accumulation is thought to cause inflammation in the body, damaging the myelin sheath.
How is ALD Inherited?
ALD is a genetic condition that may be inherited from one or both parents. ALD most severely affects males when it can either present during childhood or during adulthood. Women who are carriers for ALD develop a milder form of the disease during adulthood.
ALD Symptoms
Symptoms of ALD often begin between the ages of 4 and 10 but can also present much later in life. ALD symptoms include:
- loss of vision
- learning disabilities
- dysphagia (difficulty swallowing)
- seizures
- deafness
- lack of coordination and balance
- fatigue
- intermittent vomiting
- weight loss
- lack of appetite
- nausea
- darkening of the skin
- progressive dementia
- muscle weakness
- low blood glucose (blood sugar)
- headaches in the morning
Adrenomyeloneuropathy
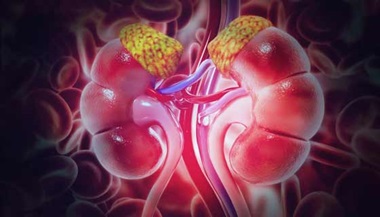
Adrenomyeloneuropathy is an adult-onset form of ALD that progresses slowly over decades. Symptoms may include a stiff gait when walking and bladder and bowel dysfunction. Many male patients often end up in need of a wheelchair. The adrenal glands often fail to produce enough steroid (cortisol) in people who have ALD, causing Addison’s disease.
ALD Diagnosis
After a thorough evaluation of the patient’s medical history, if doctors think the patient may have ALD, they will request additional testing: First, a blood test is performed to measure the levels of VLCFA. High levels of VLCFA suggest a possible ALD diagnosis. To confirm this diagnosis, a genetic test is ordered. If ALD is diagnosed, the doctor may recommend that the patient’s family members receive genetic testing. Many states have also started newborn screening for ALD.
ALD Treatment
Medications and physical therapy may be used to treat ALD symptoms. If the patient is diagnosed as a child or at an early stage of ALD, a stem cell transplant may be a promising treatment to stop the progression of ALD.
Johns Hopkins Comprehensive Adrenal Center
The Johns Hopkins Comprehensive Adrenal Center is a unique facility with world-renowned specialists in every aspect of adrenal care.